1.1.6.1. Multi-step Numerical Methods¶
Summary:
Schemes presented for linear equations are not well-suited to the solution of non-linear problems
Multi-step methods work well in non-linear hyperbolic equations
FD schemes at split time levels, also called “predictor-corrector” methods
Richtmyer/Lax-Wendroff
MacCormack
1.1.6.1.1. About Multi-step methods¶
Multi-step are FD schemes are at split time levels and work well in non-linear hyperbolic problems. They are also called predictor-corrector methods.
1st step, a “temporary value” for u(x) is “predicted”
2nd step a “corrected value” is computed
1.1.6.1.2. Richtmyer/Lax-Wendroff¶
Two variants:
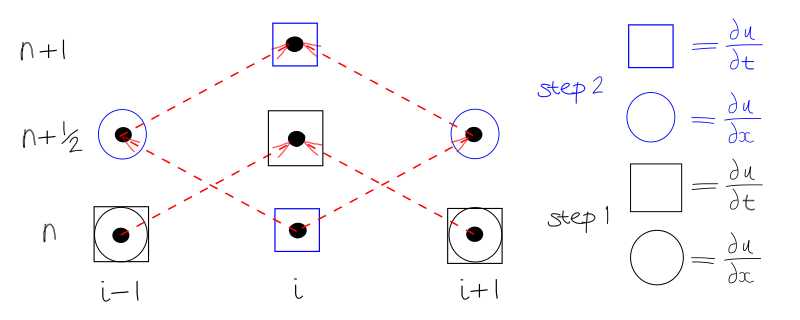
Variant 1 - Richtmyer - at point \(i\)
Variant 2 - 2 step LW - at point \(i + {1 \over 2}\)
1.1.6.1.2.1. Variant 1 - Richtmyer (Lax-Friedrichs and Leapfrog)¶
Step 1: Predictor Step use LF method at time level \(n + {1 \over 2}\)
Step 2: Corrector Step Leapfrog with \({\Delta t} \over 2\)
Transpose Step 1 and 2 for outputs:
Predictor:
Corrector:
Stable for Courant Number = \(\sigma = {{c \Delta t} \over {\Delta x}} \le 2\) (possibly as a consequence of the half-time step in the method?)
1.1.6.1.2.2. Variant 2 - 2 Step Lax-Wendroff¶
Step 1: Predictor Step use LF on \(i+{1 \over 2}\)
Step 2: Corrector Step use FTCS
Stable for Courant Number = \(\sigma = {{c \Delta t} \over {\Delta x}} \le 1\)
This scheme is 2nd order
For linear PDEs it is equivalent to the single step LW
1.1.6.1.3. MacCormack Method¶
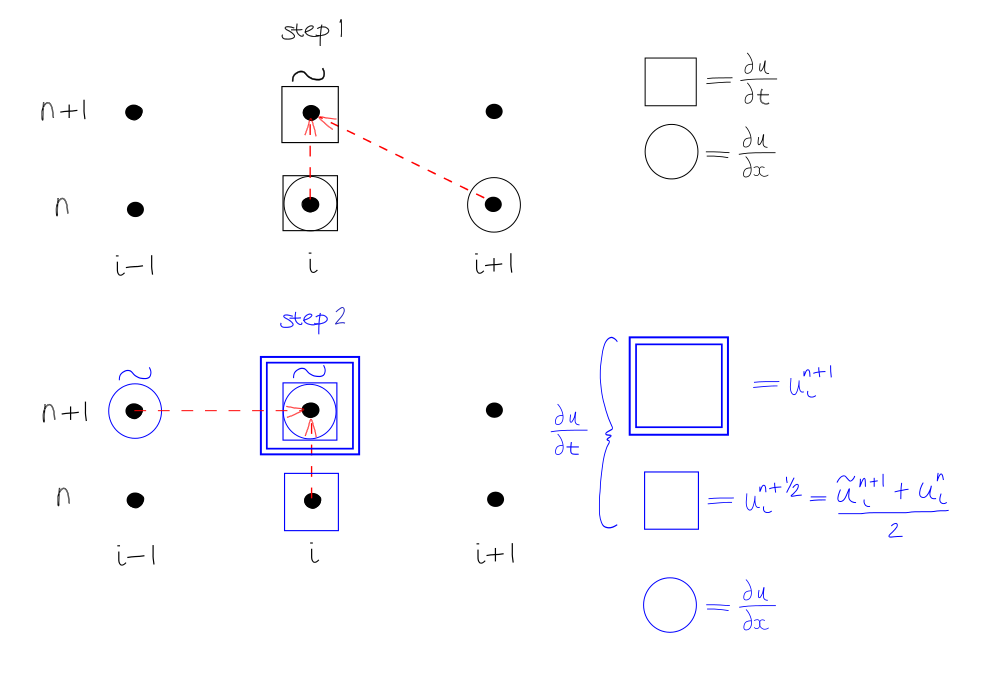
Step 1 - uses FD scheme in x - call \(\tilde{u}^{n+1}\) the temporary solution
Step 2 - uses BD scheme in x with \({{\Delta t} \over 2}\)
and replace the value \(u_i^{n+{1 \over 2}}\) by the average
Predictor
Corrector
2nd order method
Stability \(\sigma < 1\)
For linear PDEs equivalent to LW
Can alternate FD/BD - BD/FD works well for nonlinear problems
Don’t need to store values at intermediate mesh points (like 2 step Lax Wendroff)
1.1.6.1.4. Conclusion¶
The majority of PDEs in fluid mechanics are non-linear
You can learn a lot by just studying Burgers Equation, that are especially important if you are studying the Euler Equations (for compressible flows)
In general, the non-linearity dominates over viscous terms - especially in high Reynolds Number flows - but not for mixing flows, e.g. Stokes flow (where viscous terms dominate)
So studying inviscid Burgers equation has important consequences for fluid mechanics